This Neolithic period South-Western Asia began about 12,000 years ago. He marked a large turning point in human history in the transition to hunting and agricultural societies. This development caused migration in Europe and has deep changed the genetic heritage of the continent.
For a long time, North Africa was accepted as a passive actor in this transformation. The dominant score, the deposits of agriculture have never been implanted.
Some studies North African communities suggested that the adoption of agriculture in west of Nile Delta and Maghreb (existing Morocco). They continued count Hunting in the ground snail, wild plants and hunting. Then, in the Southwest Asia, the sheep and began to grow goats and local cattle.
Recently, the recent recent genetic research allowed this reconstruction in North Africa, the first to be reconstructed in the east of Maghreb (Current Tunisia and Algeria).
Simone Mulazzani. Cc by-nc-nd, Issued by the author
As a Afrikaist auditor, I specialize in work Ancient companies Through the Mediterranean Africa and Sahara. I focus on how men adapt to the environment and how the production of food production in these regions. I recently conducted an investigation with international archaeologists, geneticists and physical anthropologists to monitor old population movements in the eastern Maghreb.
Notre New research It was simply published in nature. We analyzed the ancient genomms of nine people living between 15,000 and 6,000 years in the East Maghreb (full DNA sequence).
Although the sample could seem humble, in the field of research in the old DNA, even some good genomms can also reveal great information. They serve as reference points to withdraw genetic lines and identify the ancestor links.
In addition to genetic evidence for archeological discoveries, we have reset duties, interactions and population changes for thousands of years.
Our results are surprising. These genomes clearly show that an impact of farmers has reached North Africa from the Mediterranean. However, a large part of the genetic heritage of the population of the population of the East Maghreb, the hunter remained radically in the former heritage.
These results have long a question of migration to North Africa and the idea that is seen before and during the Neolite. This allows you to deepen our understanding of the incredible complexity of past and human actions and cultural exchanges.
While continuing to investigate the genetic heritage of our fathers, such studies emphasize the complexity of human history. It is not limited to a simple change of populations in the history of agricultural history in the Mediterranean region, but the cultural, adaptation and sustainability gives results for a long time.
The study of ancient human action is not limited to better understanding of the past. This allows you to understand migration and adaptation dynamics that can help us understand similar processes today.
Production and analysis
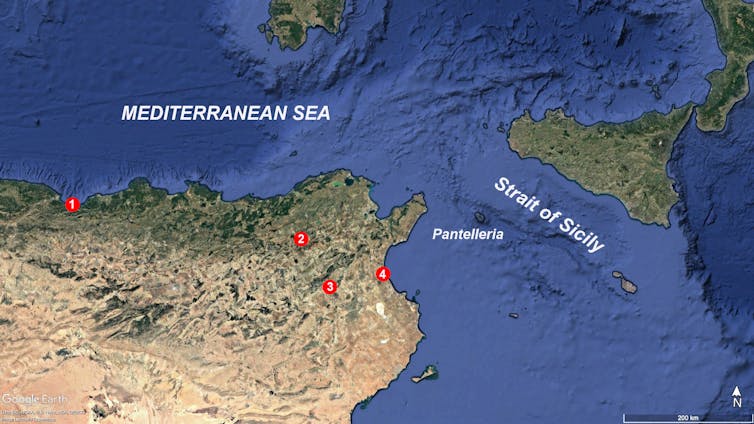
(1: Afalou Bou Rummel; 2: Djebba; 3: Doukanet El Khoutifa; 4: SHM-1, Hergla) Giulio Lucarini, CC by-NC -F, Issued by the author
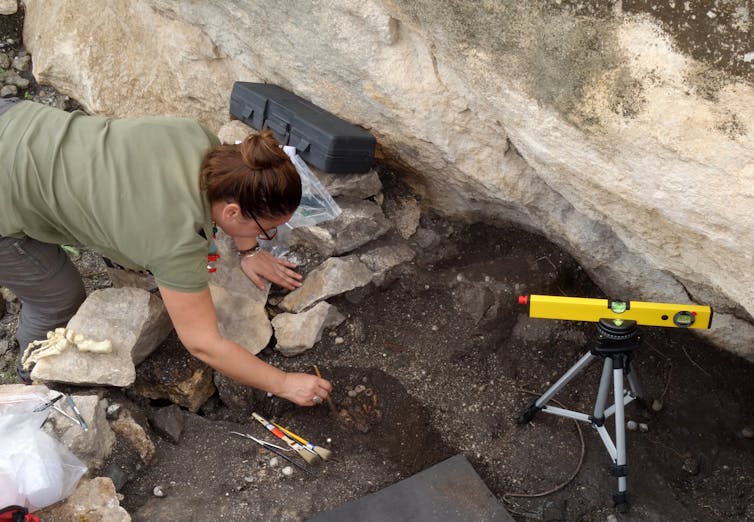
We have performed human skeletons protected in the collections of museums or inherited institutions with older genomes extract. They are excavations on four sites: Afalou Bou Rummel, Djebba, Doukanet El Khoutifa and Shm-1 (Hergla), are all located east of Maghreb.
Because they chose these patterns, because they were well preserved, it is also not always working with the old DNA.
Our analysis learned that some individuals are ancestors in Europe about 7,000 years ago. Europeans brought some genes to the region, but not more than 20% per individual.


Giulio Lucarini, CC by-nc-nnd, Issued by the author
On certain sites, a modest genetic impact compared to the old populations of Western Magbrebi, The ancestor of European farmers may reach up to 80%.
Our results do not provide results as a result of the mass replacement of the population, as the application of the food economy in eastern Maghreb. On the contrary, the change, sporadic migration, cultural beer and knowledge, gradually happened.
Between land and the sea
One of the most interesting discoveries, in Tunisia, Tunisia in Tunisia, the hunter of Europe in Tunisia was a genetic trail of the hunter, for about 8,000 years. This proposes to interact with the sea roads through Europe and North African populations passing the Sicilian Strait.
Researchers have long been announced that the cultural exchange took place through the Mediterranean. It is shown with the spread of technologies like this Pressure appliancesinstead of directing direct stone, a process to form stone tools by applying the controlled vehicle.
Discover Obsidian Tunisia (volcanic glass) PantelleriaA small island located in the throat of Sicily strengthens the connection between the northern and southern jars of the Mediterranean.
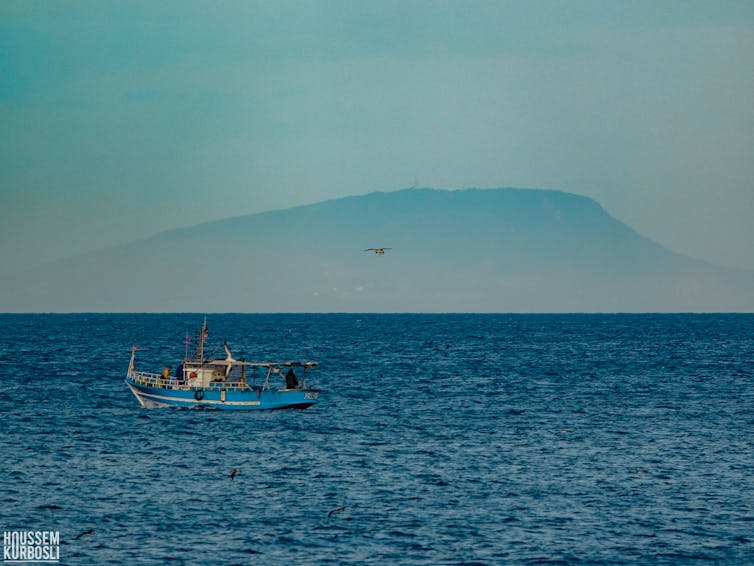


Houssem Corbosli (Forbidden Recycling), Issued by the author
Previous wooden items are rarely continues over time. This can explain that the absence of ships from this period in North Africa. But Pirogues of similar periods Central Italy (Lake Bracciano) suggests that the sea skills are well established around the Mediterranean. Although this special canoes are not directly evident between Europe and North Africa, they confirm that navigation is technically possible at that time.
The links offered by these existing evidence are genetically supported by the first time we have learned.
Another stakeholder of our research is to identify an ancestor in the east of Maghreb (in the southwestern Southwest of Asia) of the Eastern Asia. This ancestor was found in the remains of about 6,800 years. It is a genetic signature before the arrival of European farmers in several centuries. Perhaps the inner animals are testified to migration of pastoralism related to the area, which presented to the area such as sheep and goats.
Archaeological evidence in support
It is especially rewarded to note that genetic results are confirmed by archeological discoveries. This emphasizes the importance of multifaceted approaches to better understand the human dynamics of the past.
In general, our research reveals a large genetic and cultural firmness, a region marked in perfect combination Archaeological data










